Hi all,
I’m building a package and I want to support multiple languages. So I need to know what the current language is of the content I’m editing/showing in my component. And in researching this, I came across two questions:
- How do I get the variant language that I’m editing in the context of my component? This is especially important in split view!
- Whats the difference between UMB_DOCUMENT_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT and UMB_VARIANT_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT? They seems completely the same.
Getting the current app language is not difficult:
this.consumeContext(UMB_APP_LANGUAGE_CONTEXT, (instance) => {
console.log("App culture: " + instance.getAppCulture());
});
However, this is not enough in two scenario’s:
- When the node is invariant, I don’t want to have a culture, but the app culture will always have a value.
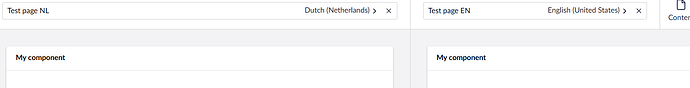
- In split view, there is more than one language.
So you can check the active variants like this:
this.consumeContext(UMB_DOCUMENT_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT, async (instance) => {
console.log("Active variants:",instance?.splitView.activeVariantsInfo);
}
This will nicely get an invariant culture when there is no vary by culture, or a culture if there is one:
![]()
![]()
Nice! However, now comes the split view scenario. Consider this:
This will give an array of active variants from the activeVariantsInfo:
![]()
That makes sense, but how on earth do I know in the context of my component what variant I’m showing/editing??
I thought that the UMB_VARIANT_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT would provide more information about the active variant compared to UMB_DOCUMENT_WORKSPACE_CONTEXT. However, they seem absolutely identical in terms of data, functions and properties. What’s the difference?